Transfer Database Task
The Transfer Database Task is used to move a database to another
SQL Server instance or create a copy on the same instance (with
different database name). This task works in two modes as shown below:
- Offline : In this mode, the source database is detached from the source server after putting it in single user mode, copies of the mdf, ndf and ldf files are moved to specified network location. On the destination server the copies are taken from the network location to the destination server and then finally both databases are attached on the source and destination servers. This mode is faster, but a disadvantage with mode is that the source database will not available during copy and move operation. Also, the person executing the package with this mode must be sysadmin on both source and destination instances.
- Online : In this mode, the task uses SMO to transfer the database objects to the destination server. In this mode, the database is online during the copy and move operation, but it will take longer as it has to copy each object from the database individually. Someone executing the package with this mode must be either sysadmin or database owner of the specified databases.
Now let me demonstrate how you can create an SSIS package with the Transfer Database Task.
Go to START -> Microsoft SQL Server 2005/2008 -> SQL Server Business Intelligence Development Studio to launch BIDS.
Then go to File menu -> New -> Project -> Select "Business
Intelligence Projects" in the left tree pane -> Select "Integration
Services Projects" and name the project as you wish and click OK.
In this new project you will see one package is already added with the
name "Package.dtsx". Drag the "Transfer Database Task" from the Toolbox
(which is normally on the left side) to the Control Flow pane. Right
click on the task and select Edit... as shown below.
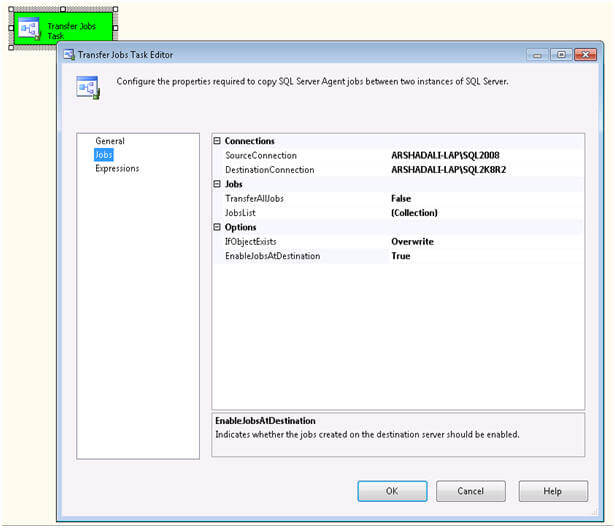
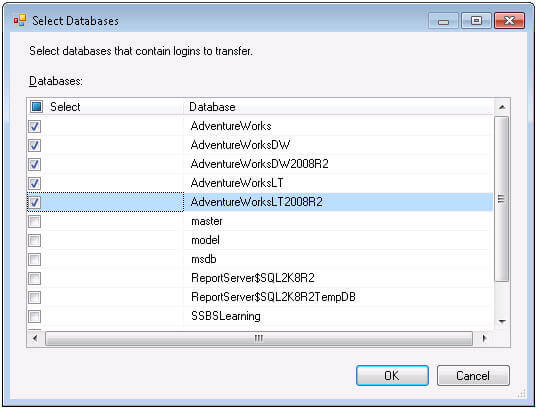
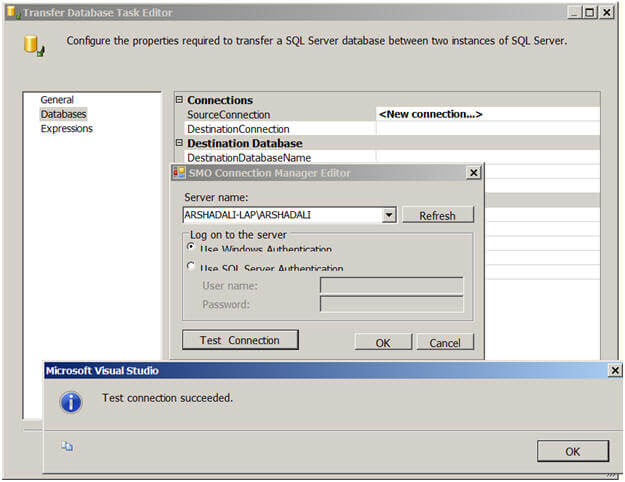
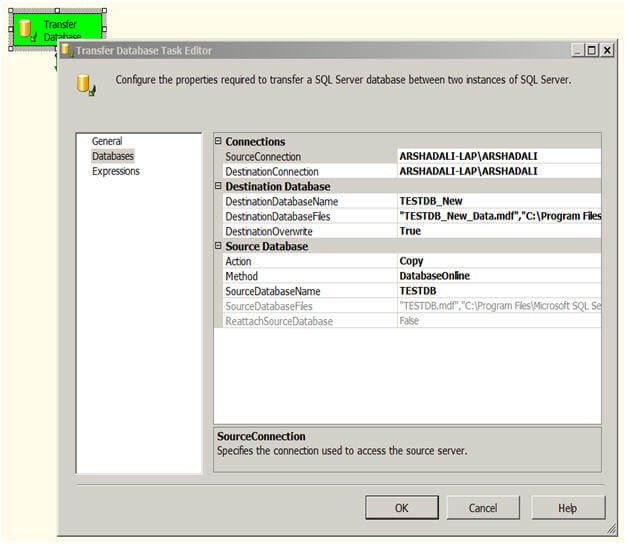
In the "Transfer Database Task Editor", select Databases on the left and
now you are ready to configure this task. SourceConnection is the
property to specify the connection for the source SQL Server instance,
if you have already created a connection manager then you can reuse it
here or can create a new one as shown below. This will also need to be
done to configure the DestinationConnection property as well.
Next you need to specify the values.
- Connections
- SourceConnection - the source instance
- DestinationConnection - the destination instance
- Destination Database
- DestinationDatabaseName - name of the new database
- DestinationDatabaseFiles - name and location of the database files
- DestinationOverwrite - if the database already exists on the destination server it will give you an error, so if you want to overwrite the destination database you can set this property to True.
- Source Database
- Action - whether you want to copy or move a database.
- Method - whether you want the copy and move operation to be offline (in this case you also need to provide the network share name which will be used to transmit the database files.
- SourceDatabaseName - name of the source database
- SourceDatabaseFiles - name and location of the database files
- ReattachSourceDatabase - is another property which you can set to TRUE to reattach the source database after the copy operation.
Once you are done with all these configurations you can hit F5 or click
on the play icon to execute the package. Your task will turn yellow
during the execution and then either red or green depending on the
execution outcome. You can go to progress tab to see error messages if
the execution fails. Although failure is rare, it is possible if your
source database is smaller than the size of the model database on the
destination server.
You can also use Copy Database Wizard to copy and move your database, for details refer to Upgrading to SQL Server 2008 using Copy Database Wizard.
Transfer SQL Server Objects Task
The Transfer SQL Sever Objects task is used to transfer one or
more SQL Server objects to a different database, either on the same or
another SQL Server instance. This allows you to select different types
of objects you want to transfer. You can select tables, views, stored
procedures, user defined functions etc. Not only this, you can select a
combination of these types of objects to transfer and even select
particular objects of a particular object type.
Create another package in the same project and drag a "Transfer SQL
Server Objects Task" to the Control Flow. Right click on the task and
then select Edit. In the "Transfer SQL Server Objects Task Editor" click
on Objects to set the different properties for this task as shown
below.
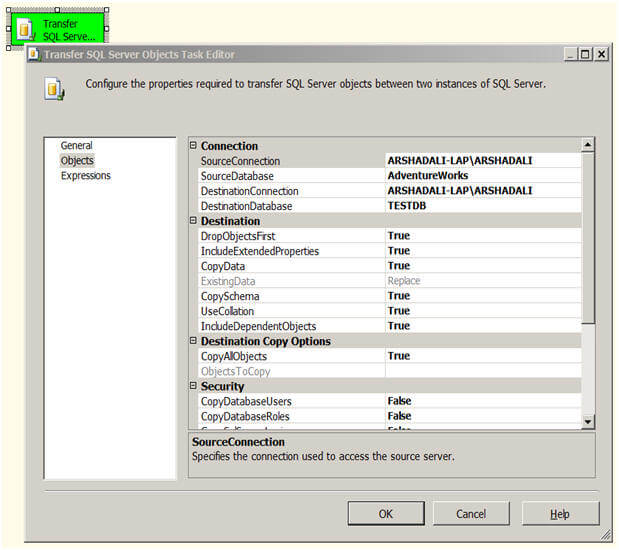
Similar to the way you configured the SourceConnection and
DestinationConnection for the Transfer Database Task, you need to
configure these properties for this task as well. SourceDatabase is the
name of the database from where you are copying the objects and
DestinationDatabase is the name of the database to which you are copying
the objects to.
- Connection
- SourceConnection - the source instance
- SourceDatabase - name of the source database
- DestinationConnection - the destination instance
- DestinationDatabase - name of the new database
- Destination
- DropObjectsFirst - Drop selected objects on the target before copy
- IncludeExtendedProperties - While copying operation also include extended properties of SQL objects being copied
- CopyData - While copying tables, transfer the data of the selected tables as well
- ExistingData - whether to append or replace data
- CopySchema - Copy the schema of the objects being copied
- UseCollation - Make sure collation of the columns are appropriately set on copied tables
- IncludeDependentObjects - Include all the objects in copy operation which are dependent on selected objects
- Destination Copy Objects
- CopyAllObjects - Do you want to copy all objects from the source database, if set to False, next property ObjectsToCopy will get enabled.
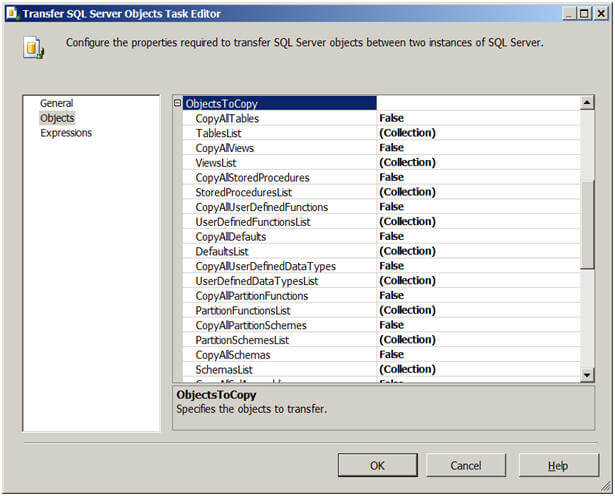
- ObjectsToCopy - With this property you select types of objects you want to copy. You can select all objects of one or more types or select particular objects as you can see in the below image. Depending on the SQL Server version, type of objects selection will vary.
- Security
- CopyDatabaseUsers - whether to include users
- CopyDatabaseRoles - whether to include roles
- CopySQLServerLogins - whether to include logins
- CopyObjectLevelPermissions - whether to include object level permissions
- Table Options
- CopyIndexes - whether to include indexes
- CopyTriggers - whether to include triggers
- CopyFullTextIndexes - whether to include full text indexes
- CopyAllDRIObjects - whether to include referential integrity objects
- CopyPrimaryKeys - whether to include primary keys
- CopyForeignKeys - whether to include foreign keys
- GenerateScriptsInUnicode - whether to create script in Unicode or not
Below is a partial listing of the objects that can be selected.
The person executing the package with this task must have at least
browse objects permissions on the source database and on the destination
database must have permissions to drop and create objects.